利用python进行数值分析代码示例
作者:袖梨
2022-06-25
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下利用python进行数值分析代码示例,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
一、准备
噪声是在拟合过程中常用的干扰手段,常用的噪声:
1.统一分布 U(a,b)
f ( x ) = { 1 i f a ≤ x < b 0 o t h e r f(x)=begin{cases}begin{aligned}1&quad ifquad ale x
import numpy as np
x=np.random.uniform(a,b,100) #产生长度为100的U(a,b)
2.正态分布N( μ mu μ, σ 2 sigma^2 σ2)
import numpy as np x=np.random.normal(mu, sig, 100) #产生长度为100的N(mu, sqart(sig))
二、三次样条插值
def spline_fit():
size = 20
x = np.linspace(-10, 10, size)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.normal(0, 0.1, size)
y2 = [0] * len(y)
# for y_i in y:
pp.plot(x, y)
cs = CubicSpline(x, y)
x2 = x = np.linspace(-10, 10, size * 100)
pp.plot(x2, cs(x2))
pp.show()
三、最小二乘拟合
def least_square():
f = lambda p0, xx: p0[0] * np.sin(xx * p0[1]) + p0[2]
LEN = 100
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, LEN)
y = x ** 2 + 5
# 默认情况,param只会返回求得的参数和返回的错误码,1-4为成功,5-8为失败,如果想输出更多参数,可以指定full_out=1,可以看到出错原因和其他参数
param = leastsq(lambda p0, xx, yy: f(p0, xx) - yy, (1, 1, 1), args=(x, y)) #初值的选择比较重要,如果选取不当,容易陷入局部最优
print(param)
pp.scatter(x, y)
p0 = param[0]
pp.plot(x, f(p0, x))
pp.show()
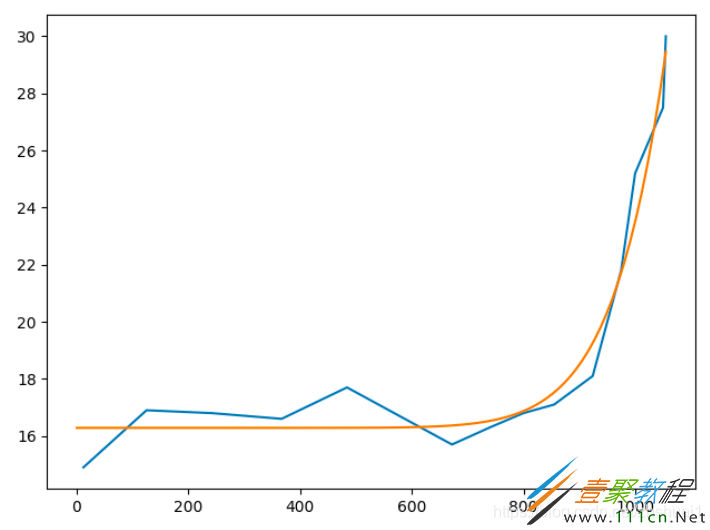
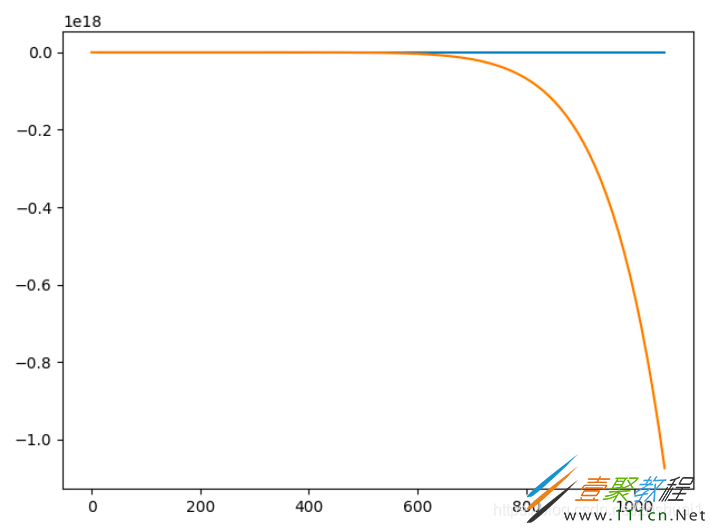
最小二乘的初值选取非常重要,以下是三份完全相同的数据,虽然最后都收敛了,但是初值不同,得到了完全不同的拟合结果
初值为 ( 1 , 2 , 1 ) (1,2,1) (1,2,1)
初值为 ( 1 , 1 , 1 ) (1,1,1) (1,1,1)
初值为 ( 10 , 10 , 1 ) (10,10,1) (10,10,1)
四、拉格朗日乘子法
def lagrange()
from scipy.optimize import minimize
import numpy as np
e = 1e-10
fun = lambda x: 8 * (x[0] * x[1] * x[2]) # f(x,y,z) =8 *x*y*z
cons = ({'type': 'eq', 'fun': lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + x[1] ** 2 + x[2] ** 2 - 1}, # x^2 + y^2 + z^2=1
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': lambda x: x[0] - e}, # x>=e等价于 x > 0
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': lambda x: x[1] - e},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': lambda x: x[2] - e}
)
x0 = np.array((1.0, 1.0, 1.0)) # 设置初始值
res = minimize(fun, x0, method='SLSQP', constraints=cons)
print('最大值:', res.fun)
print('最优解:', res.x)
print('迭代终止是否成功:', res.success)
print('迭代终止原因:', res.message)