使用自定义注解+springAop实现参数非空校验方式代码示例
作者:袖梨
2022-06-29
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下使用自定义注解+springAop实现参数非空校验方式代码示例,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
自定义注解+springAop参数非空校验
自定义注解,来对对应的方法进行入参校验,为空返回参数错误
新建注解类@interface ParamsVerify
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//枚举,表示注解可能出现在的地方
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行时保留注解
@Documented//生成api文档时会看到此注解,可加可不加
public @Interface ParamsVerify(){
//注解类修饰符必须是public 如果不写会默认public
String[] params() default "";//传入方法的参数
}
利用springAop来实现切面
利用springAop,我们可以把除业务核心代码以外的,需要重复进行的操作来统一处理,例如打印日志,参数校验等等,以切面的方式来进行,一个切面,由切点、通知(增强)来组成
增强就是对Aop管理的代码来通过动态代理来添加额外的逻辑(代码),动态代理有两种实现方式,一种是通过jdk,一种是通过cglib,springboot中默认是使用cglib来进行动态代理的;而切点(ponitCut),是多个连接点组成的一个切点,通常通过表达式来指向程序中一个定义的位置,来告知springAop启动的范围
//这个切点定义为使用该注解的方法都可以执行该切面类里的通知
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.xy.utlis.annotations.TestA)")
新建一个切面类
通知方法执行顺序
环绕–前置—后置
@Aspect//声明该类是一个切面类
@Component//声明该类交由spring管理
public class testAImpl {
/** 定义切点,使用该TestA注解的方法 */
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.xy.utlis.annotations.TestA)")
public void addAdvice(){
}
@Aroud("addAdvice")//环绕通知 另外还有@Before @After
public Object test(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕方法开始执行....");
//获取所有参数名
String[] parameterNames = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames();
//获取所有参数值
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
//获取当前注解下的方法
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
//根据当前方法获取注解
TestA annotation = signature.getMethod().getAnnotation(TestA.class);
String[] names = annotation.params();//获得注解参数
Map params = params(joinPoint);
for (String name : names) {
Object o = params.get(name);
if(null==o||"".equals(o)){
System.err.println(MessageFormat.format("参数名为{0}的值为null",name));
return false;
}
}
System.out.println("环绕方法结束执行....");
return joinPoint.proceed();//继续正常执行方法
}
}
写一个接口来测试是否成功
@PostMapping("test")
@TestA(params={"name","age","sex"})//表明这三个参数是必填的
public void test(String name,String age,String sex){
System.out.println("ok");
}
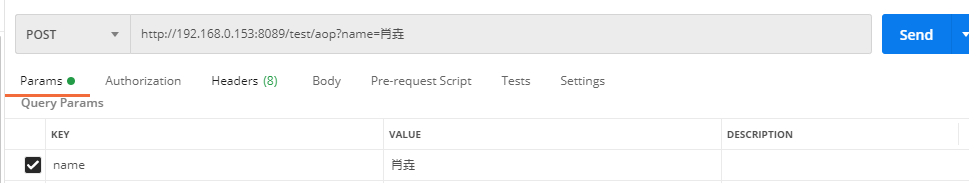
发送post请求,只携带name
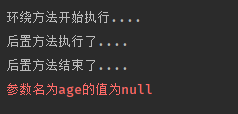
检测到参数为null,打印错误信息
这里可以自定义返回异常值或者其他处理了
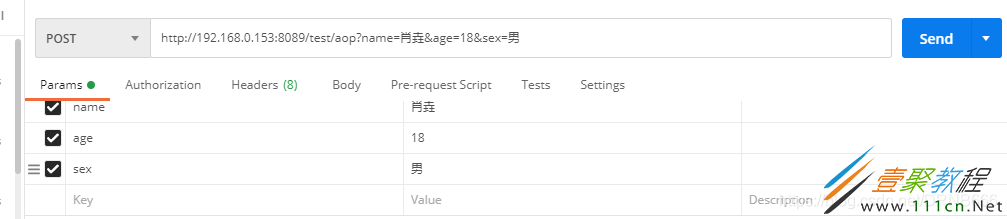
带上完整参数请求接口
成功放行
使用注解统一校验参数非空
可修改做工具类
代码:
1. 待校验类
public class User {
@NonNull(content = "姓名不能为空", minLen = 2, maxLen = 100)
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
2. 注解类
@Documented
@Target(value = ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface NonNull {
String name() default "";
String content() default "";
int maxLen() default 50;
int minLen() default 1;
}
3. 校验
public void test() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("老王");
try {
valid(user);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void valid(T user) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Class clazz = user.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
validParams(user, methods, field);
}
System.out.println("==========参数校验通过=========");
}
private void validParams(T user, Method[] methods, Field field) throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
NonNull annotation = field.getAnnotation(NonNull.class);
String fieldName;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(annotation.name())) {
fieldName = annotation.name();
} else {
fieldName = field.getName();
}
for (Method method : methods) {
if (("get" + fieldName).toLowerCase().equals(method.getName().toLowerCase())) {
Object getMethodResult = method.invoke(user, null);
if (getMethodResult == null) {
System.out.println("==========非Null校验失败=========");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("[" + annotation.content() + "]为null");
}
if (getMethodResult instanceof String) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(String.valueOf(getMethodResult))) {
System.out.println("==========非空校验失败=========");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("[" + annotation.content() + "]为空");
}
System.out.println(fieldName + "长度:" + String.valueOf(getMethodResult).length());
if (String.valueOf(getMethodResult).length() > annotation.maxLen()) {
System.out.println("==========长度超出指定范围=========");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("[" + fieldName + "]长度超出");
}
if (String.valueOf(getMethodResult).length() < annotation.minLen()) {
System.out.println("==========长度小于指定范围=========");
throw new IllegalArgumentException("[" + fieldName + "]长度不够");
}
}
}
}
}
结果参考:
name长度:2
==========参数校验通过=========
name长度:2
==========长度小于指定范围=========