SpringBoot为何可以使用Jar包启动代码解析
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下SpringBoot为何可以使用Jar包启动代码解析,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
Spring Boot 打包插件
Spring Boot 提供了一个名叫spring-boot-maven-plugin的 maven 项目打包插件,如下:
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin
可以方便的将 Spring Boot 项目打成 jar 包。 这样我们就不再需要部署 Tomcat 、Jetty等之类的 Web 服务器容器啦。
我们先看一下 Spring Boot 打包后的结构是什么样的,打开 target 目录我们发现有两个jar包:
其中,springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar是通过 Spring Boot 提供的打包插件采用新的格式打成 Fat Jar,包含了所有的依赖;
而springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.original则是Java原生的打包方式生成的,仅仅只包含了项目本身的内容。
SpringBoot FatJar 的组织结构
我们将 Spring Boot 打的可执行 Jar 展开后的结构如下所示:
BOOT-INF目录:包含了我们的项目代码(classes目录),以及所需要的依赖(lib 目录);
META-INF目录:通过MANIFEST.MF文件提供 Jar包的元数据,声明了 jar 的启动类;
org.springframework.boot.loader:Spring Boot 的加载器代码,实现的 Jar in Jar 加载的魔法源。
我们看到,如果去掉BOOT-INF目录,这将是一个非常普通且标准的Jar包,包括元信息以及可执行的代码部分,其/META-INF/MAINFEST.MF指定了Jar包的启动元信息,org.springframework.boot.loader执行对应的逻辑操作。
MAINFEST.MF 元信息
元信息内容如下所示:
Manifest-Version: 1.0 Spring-Boot-Classpath-Index: BOOT-INF/classpath.idx Implementation-Title: springboot Implementation-Version: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT Spring-Boot-Layers-Index: BOOT-INF/layers.idx Start-Class: com.listenvision.SpringbootApplication Spring-Boot-Classes: BOOT-INF/classes/ Spring-Boot-Lib: BOOT-INF/lib/ Build-Jdk-Spec: 1.8 Spring-Boot-Version: 2.5.6 Created-By: Maven Jar Plugin 3.2.0 Main-Class: org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher
它相当于一个 Properties 配置文件,每一行都是一个配置项目。重点来看看两个配置项:
Main-Class 配置项:Java 规定的 jar 包的启动类,这里设置为 spring-boot-loader 项目的 JarLauncher 类,进行 Spring Boot 应用的启动。
Start-Class 配置项:Spring Boot 规定的主启动类,这里设置为我们定义的 Application 类。
Spring-Boot-Classes 配置项:指定加载应用类的入口。
Spring-Boot-Lib 配置项: 指定加载应用依赖的库。
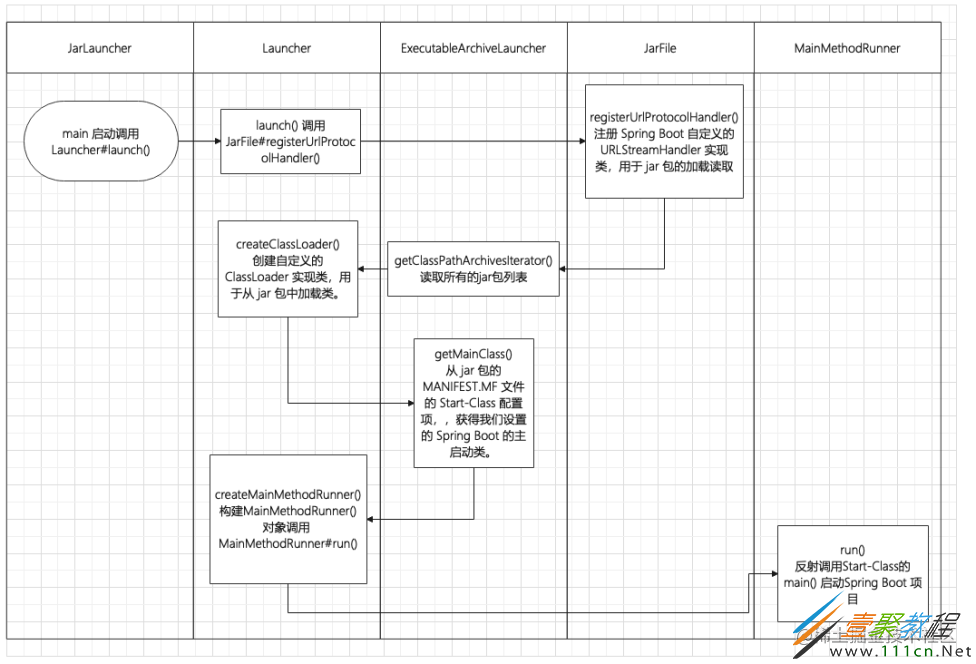
启动原理
Spring Boot 的启动原理如下图所示:
源码分析
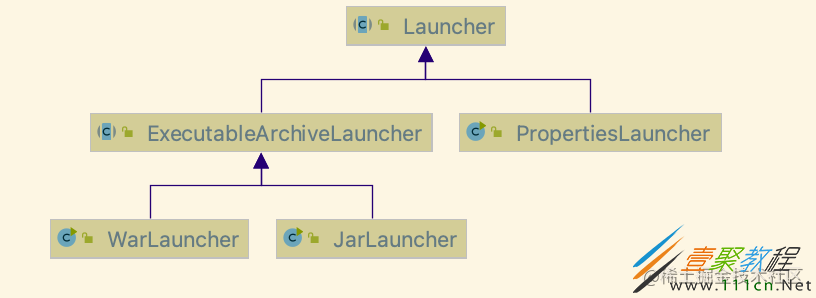
JarLauncher
JarLauncher 类是针对 Spring Boot jar 包的启动类, 完整的类图如下所示:
其中的 WarLauncher 类,是针对 Spring Boot war 包的启动类。 启动类org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher并非为项目中引入类,而是spring-boot-maven-plugin插件 repackage 追加进去的。
接下来我们先来看一下 JarLauncher 的源码,比较简单,如下图所示:
public class JarLauncher extends ExecutableArchiveLauncher {
private static final String DEFAULT_CLASSPATH_INDEX_LOCATION = "BOOT-INF/classpath.idx";
static final EntryFilter NESTED_ARCHIVE_ENTRY_FILTER = (entry) -> {
if (entry.isDirectory()) {
return entry.getName().equals("BOOT-INF/classes/");
}
return entry.getName().startsWith("BOOT-INF/lib/");
};
public JarLauncher() {
}
protected JarLauncher(Archive archive) {
super(archive);
}
@Override
protected ClassPathIndexFile getClassPathIndex(Archive archive) throws IOException {
// Only needed for exploded archives, regular ones already have a defined order
if (archive instanceof ExplodedArchive) {
String location = getClassPathIndexFileLocation(archive);
return ClassPathIndexFile.loadIfPossible(archive.getUrl(), location);
}
return super.getClassPathIndex(archive);
}
private String getClassPathIndexFileLocation(Archive archive) throws IOException {
Manifest manifest = archive.getManifest();
Attributes attributes = (manifest != null) ? manifest.getMainAttributes() : null;
String location = (attributes != null) ? attributes.getValue(BOOT_CLASSPATH_INDEX_ATTRIBUTE) : null;
return (location != null) ? location : DEFAULT_CLASSPATH_INDEX_LOCATION;
}
@Override
protected boolean isPostProcessingClassPathArchives() {
return false;
}
@Override
protected boolean isSearchCandidate(Archive.Entry entry) {
return entry.getName().startsWith("BOOT-INF/");
}
@Override
protected boolean isNestedArchive(Archive.Entry entry) {
return NESTED_ARCHIVE_ENTRY_FILTER.matches(entry);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//调用基类 Launcher 定义的 launch 方法
new JarLauncher().launch(args);
}
}
主要看它的 main 方法,调用的是基类 Launcher 定义的 launch 方法,而 Launcher 是ExecutableArchiveLauncher的父类。下面我们来看看Launcher基类源码:
Launcher
public abstract class Launcher {
private static final String JAR_MODE_LAUNCHER = "org.springframework.boot.loader.jarmode.JarModeLauncher";
protected void launch(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (!isExploded()) {
JarFile.registerUrlProtocolHandler();
}
ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(getClassPathArchivesIterator());
String jarMode = System.getProperty("jarmode");
String launchClass = (jarMode != null && !jarMode.isEmpty()) ? JAR_MODE_LAUNCHER : getMainClass();
launch(args, launchClass, classLoader);
}
@Deprecated
protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(List archives) throws Exception {
return createClassLoader(archives.iterator());
}
protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(Iterator archives) throws Exception {
List urls = new ArrayList<>(50);
while (archives.hasNext()) {
urls.add(archives.next().getUrl());
}
return createClassLoader(urls.toArray(new URL[0]));
}
protected ClassLoader createClassLoader(URL[] urls) throws Exception {
return new LaunchedURLClassLoader(isExploded(), getArchive(), urls, getClass().getClassLoader());
}
protected void launch(String[] args, String launchClass, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Exception {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
createMainMethodRunner(launchClass, args, classLoader).run();
}
protected MainMethodRunner createMainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args, ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new MainMethodRunner(mainClass, args);
}
protected abstract String getMainClass() throws Exception;
protected Iterator getClassPathArchivesIterator() throws Exception {
return getClassPathArchives().iterator();
}
@Deprecated
protected List getClassPathArchives() throws Exception {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected call to getClassPathArchives()");
}
protected final Archive createArchive() throws Exception {
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getClass().getProtectionDomain();
CodeSource codeSource = protectionDomain.getCodeSource();
URI location = (codeSource != null) ? codeSource.getLocation().toURI() : null;
String path = (location != null) ? location.getSchemeSpecificPart() : null;
if (path == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive");
}
File root = new File(path);
if (!root.exists()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to determine code source archive from " + root);
}
return (root.isDirectory() ? new ExplodedArchive(root) : new JarFileArchive(root));
}
protected boolean isExploded() {
return false;
}
protected Archive getArchive() {
return null;
}
}
launch 方法会首先创建类加载器,而后判断是否 jar 是否在MANIFEST.MF文件中设置了jarmode属性。
如果没有设置,launchClass 的值就来自getMainClass()返回,该方法由PropertiesLauncher子类实现,返回 MANIFEST.MF 中配置的Start-Class属性值。
调用createMainMethodRunner方法,构建一个MainMethodRunner对象并调用其 run 方法。
PropertiesLauncher
@Override
protected String getMainClass() throws Exception {
//加载 jar包 target目录下的 MANIFEST.MF 文件中 Start-Class配置,找到springboot的启动类
String mainClass = getProperty(MAIN, "Start-Class");
if (mainClass == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No '" + MAIN + "' or 'Start-Class' specified");
}
return mainClass;
}
MainMethodRunner
目标类main方法的执行器,此时的 mainClassName 被赋值为 MANIFEST.MF 中配置的 Start-Class 属性值,也就是com.listenvision.SpringbootApplication,之后便是通过反射执行 SpringbootApplication 的 main 方法,从而达到启动 Spring Boot 的效果。
public class MainMethodRunner {
private final String mainClassName;
private final String[] args;
public MainMethodRunner(String mainClass, String[] args) {
this.mainClassName = mainClass;
this.args = (args != null) ? args.clone() : null;
}
public void run() throws Exception {
Class mainClass = Class.forName(this.mainClassName, false, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader());
Method mainMethod = mainClass.getDeclaredMethod("main", String[].class);
mainMethod.setAccessible(true);
mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { this.args });
}
}