Silverlight之文件上传组件
主要内容:
一、组件特点
二、实现原理
三、编码实现
一、组件特点
对于今天要说的组件姑且叫做"CmjUpload"吧,方便称呼。目前有很多上传组件来辅助完成日常开发,"CmjUpload"有什么特点呢:
- 解决大文件、多文件上传问题
- 基于asp.net上传,不需要部署WCF、WebService操作方便
- 接口丰富、灵活性强,配置使用方便。
- 支持选择、拖拽两种文件添加方式上传,用户体验好。
- 支持取消、暂停、继续操作满足续传要求。
OK,就说那么多吧,主要是让大家有兴趣看下去,其实之所以有今天的话题主要还是为了学习以及满足实际开发需求。
二、实现原理
在Silverlight中要实现上传有很多方式,例如说使用WCF或者WebService,但是考虑到实际情况,这里没有选择以上两种方式,而是选择了WebRequest方式。原因比较简单,部署十分方便,不需要为了上传组件而进行额外的配置。Silverlight中使用WebRequest同其他.Net开发中的使用方式是类似的,不同的是Silverlight中很多操作都是异步的,当然WebRequest也不例外。此外,在这里需要对一个文件分块发送,一方面可以解决大文件上传问题,另一方面可以实时显示文件上传进度。下面一个简单的交互过程:
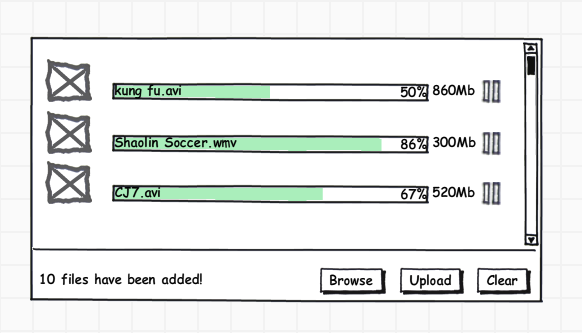
当然要完成整个组件远不止上面说的这些,UI的设计,组件的本地化,用户接口的设计等都是必须思考的问题。下面是组件界面原型:
界面分为两个区域:文件显示区域和操作区域,当然这里的文件区域本身也是可以操作的,例如如果你不想点击按钮选择文件的话,可以选择直接拖拽一个或多个文件到文件区域。还可以对已添加的文件进行删除操作,对正在上传的文件进行暂停和续传操作。此外文件区域的设计主要提供文件信息显示,例如缩略图、上传进度、文件名称、文件大小等信息。操作区域一方面提供文件整体信息的显示(例如文件总数、已上传数等),另一方面提供了文件浏览、上传、清空操作。
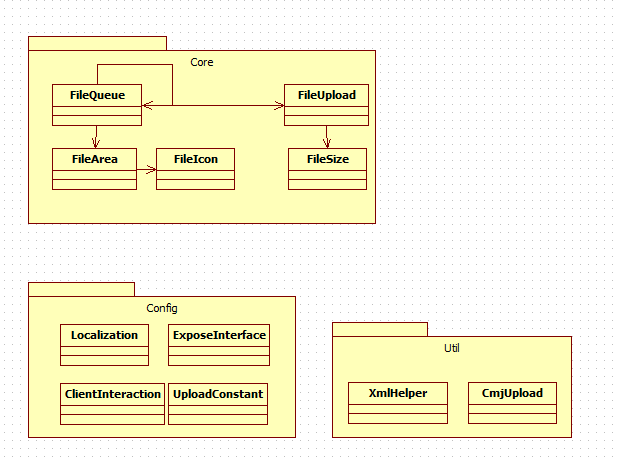
下面是类的设计:
在上图中我们可以看出有三个包:Core、Config、Util。
Core是核心包,里面主要包括文件队列管理(FileQueue)、文件上传控制(FileUpload)、文件界面区域(FileArea)、文件大小单位转换(FileSize)、缩略图控制(FileIcon)。
Config是配置和接口包,主要包括组件设计级别常量(注意不是用户级别也不是开发级别,开发级别配置在接口中进行)(UploadConstant)、客户端开发接口(ExposeInterface)、本地化实现(Localization)、接口注册(ClientInteraction)。
Util包主要包括一些常用辅助类,主要包括xml操作(XmlHelper)、服务器端文件保存辅助类(CmjUpload)。
三、编码实现
有了上面的分析相信下面的实现就相当容易理解了,首先看一下文件上传类FileUpload:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Documents;
using System.Windows.Ink;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation;
using System.Windows.Shapes;
using System.Text;
using System.IO;
using System.Windows.Threading;
using CmjUpload.Util;
using CmjUpload.Config;
namespace CmjUpload
{ public class FileUpload
{
//开始上传
public delegate void StartUploadHanler(object sender,EventArgs e);
public event StartUploadHanler StartUpload;
public void OnStartUpload(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (StartUpload != null)
{
StartUpload(sender, e);
}
}
// 上传
public delegate void UploadingHanler(object sender, ProgressArgs e);
public event UploadingHanler Uploading;
public void OnUploading(object sender, ProgressArgs e)
{
if (Uploading != null)
{
Uploading(sender,e);
}
}
//上传结束
public delegate void UploadCompletedHanler(object sender, EventArgs e);
public event UploadCompletedHanler UploadCompleted;
public void OnUploadCompleted(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (UploadCompleted != null)
{
UploadCompleted(sender, e);
}
}
private string _fileName = "";
private long _fileLength = 0;
private long _blockLength = 4096;//单次上传文件大小
private long _postedLength = 0;//已传输文件大小
private long _nextLength = 0;//下次传输的文件大小
private bool _firstUpload = true;
private BinaryReader _fileReader = null;
private UploadStatus _uploadStatus = UploadStatus.Start;
public FileInfo File
{
get;
set;
}
//public long PostedLength
//{
// get
// {
// return _postedLength;
// }
// set
// {
// _postedLength = value;
// }
//}
public UploadStatus Status
{
get
{
return _uploadStatus;
}
set
{
_uploadStatus = value;
}
}
public void Upload(FileInfo file)
{
this.File = file;
//XmlHelper xmlHelper = new XmlHelper("Config/CmjUploadConfig.xml");
//_requestUrl=xmlHelper.GetAttibuteValue("Upload", "RequestUrl");
_requestUrl = ExposeInterface.Instance().RequestUrl;
this._fileName = this.File.Name;
this._fileLength = this.File.Length;
this._blockLength = FileSize.GetLockSize(this._fileLength);
//this._postedLength = 0;
_fileReader = new BinaryReader(file.OpenRead());
//_uploadStatus = UploadStatus.Start;
if (_fileLength
{
_nextLength = _fileLength;
}
else
{
_nextLength = _blockLength;
}
OnStartUpload(this, new EventArgs());
UploadInBlock();
}
public void UploadInBlock()//上传一块数据
{
UriBuilder uriBuilder = new UriBuilder(new Uri(_requestUrl, UriKind.Absolute));
uriBuilder.Query = string.Format("fileName={0}&status="+_uploadStatus,this._fileName);
WebRequest request = WebRequest.Create(uriBuilder.Uri);
request.Method = "POST";
request.ContentType = "multipart/mixed";//注意这里
request.ContentLength = _nextLength;
if (_firstUpload)
{
_uploadStatus = UploadStatus.Uploading;
_firstUpload = false;
}
request.BeginGetRequestStream((IAsyncResult asyncResult) =>
{
WebRequest rqst = asyncResult.AsyncState as WebRequest;
Stream rqstStm = rqst.EndGetRequestStream(asyncResult);
byte[] buffer = new byte[_blockLength];
int size = _fileReader.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
if(size>0)
{
rqstStm.Write(buffer, 0, size);
rqstStm.Flush();
_postedLength += size;
if ((_fileLength - _postedLength)
{
_nextLength = _fileLength-_postedLength;
}
}
rqstStm.Close();
rqst.BeginGetResponse((IAsyncResult ascResult) =>//开始数据传输
{
OnUploading(this, new ProgressArgs() { Percent = ((double)_postedLength / (double)_fileLength) });
WebRequest webRequest = ascResult.AsyncState as WebRequest;
WebResponse webResponse = (WebResponse)webRequest.EndGetResponse(ascResult);
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(webResponse.GetResponseStream());
string responsestring = reader.ReadToEnd();
reader.Close();
if (_postedLength >= _fileLength)
{
_uploadStatus = UploadStatus.Complelte;
}
if (_uploadStatus == UploadStatus.Uploading)
{
UploadInBlock();
}
//else if(_uploadStatus==UploadStatus.Cancel)
//{
// return;
//}
else if (_uploadStatus==UploadStatus.Complelte)
{
_fileReader.Close();
OnUploadCompleted(this, new EventArgs());
}
}, request);
}, request);
}
///
/// 继续上传
///
///
///
//public static void ContinueUplaod(string fileName,long uploadedLength)
//{
//}
}
//上传进度参数
public class ProgressArgs:EventArgs
{
public double Percent
{
get;
set;
}
}
public enum UploadStatus
{
Start,
Uploading,
Cancel,
Complelte
}
} |
在这个类中需要注意的是状态的控制,因为组件需要实现文件暂停、续传功能,并且每次请求时需要发送相应的操作状态;另一点就是对外公开了三个事件,用于给UI提供进度支持和状态通知。
FileQueue管理整个文件队列,控制着界面UI、文件上传等信息:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
namespace CmjUpload
{ ///
/// 文件队列管理者
///
public class FileQueue
{
private static object _lock = new object();
private static FileQueue _fileQueue = null;
private Dictionary
private Dictionary
private Dictionary
private Dictionary
|